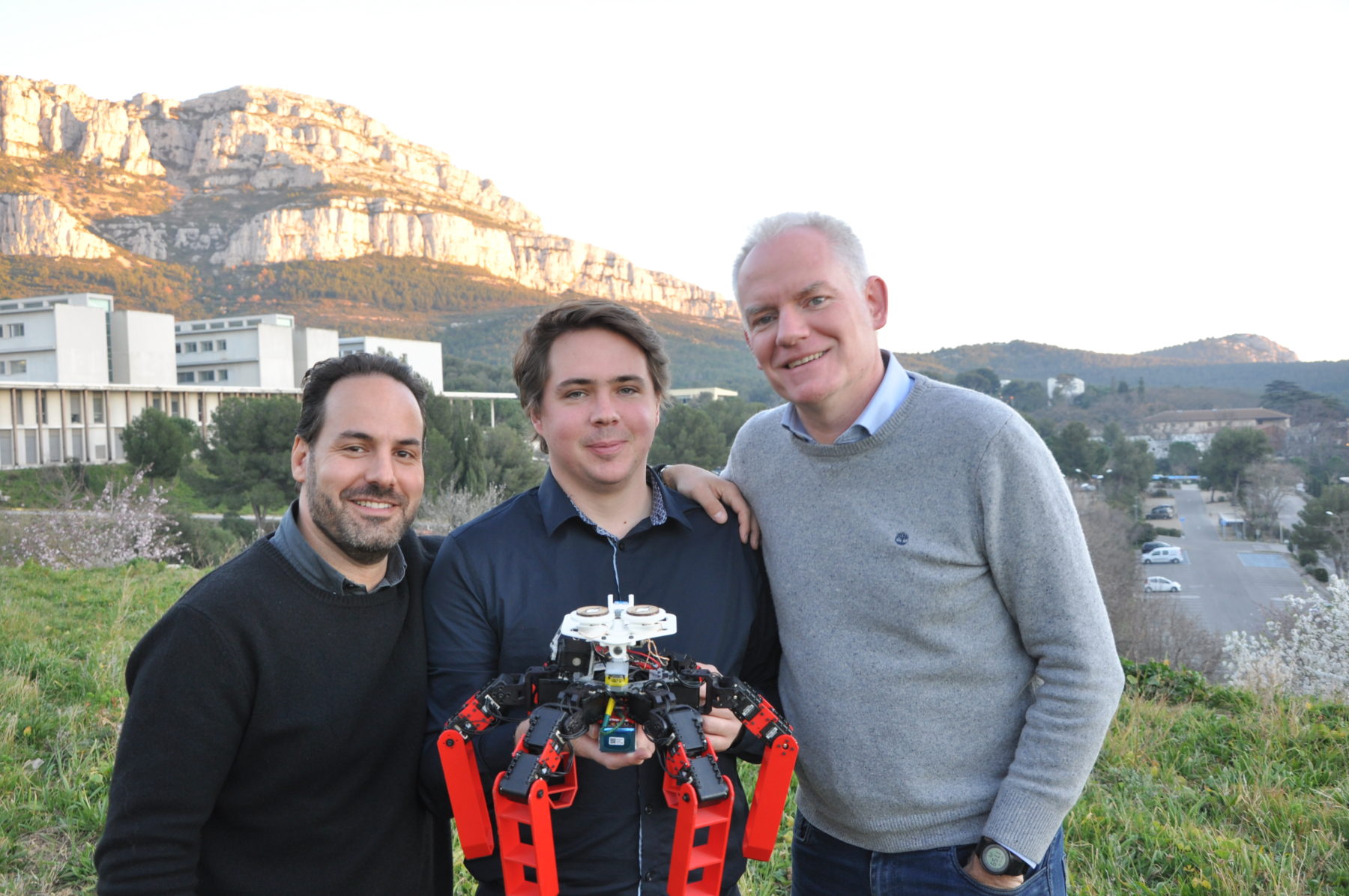
The Hexapod Robot AntBot
AntBot, a robot ant capable of navigating outdoors and autonomously, without GPS with only 14 pixels.
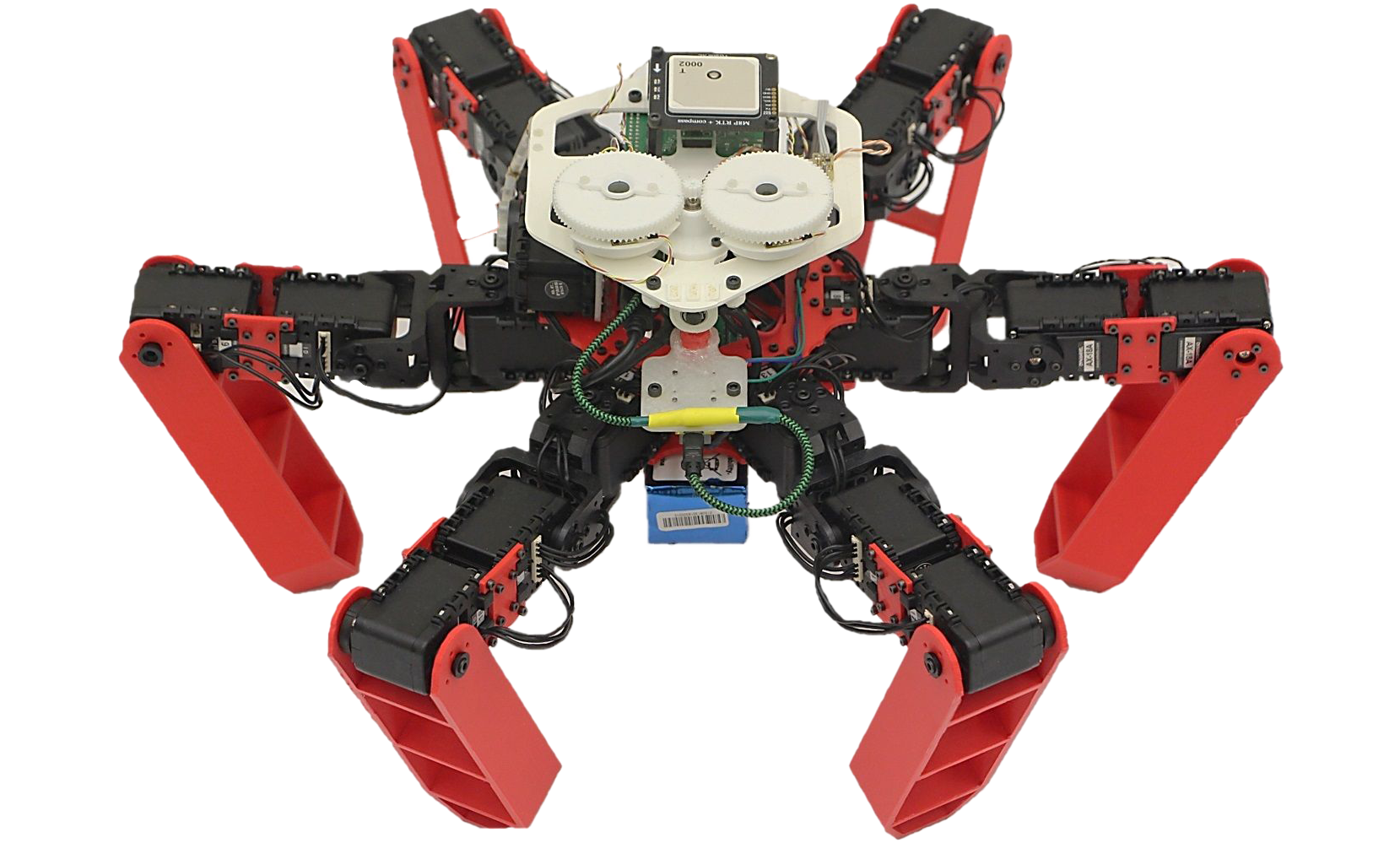
Objective of the AntBot project
AntBot’s objective is to show that it is possible to navigate autonomously outdoors, without using GPS and with very few resources while ensuring precision, robustness and resilience with regard to environmental conditions. This insectoid robot is inspired by desert ants Cataglyphis fortis in many ways respects.
The AntBot robot was developed as part of the thesis of Julien Dupeyroux (2015-2019, ISM – AMU/CNRS) which I co-directed with Stéphane Viollet. AntBot is a 3D printed hexapod robot and totally open-source.
Publications
- Dupeyroux, J., Viollet, S., & Serres, J. R. (2019). An ant-inspired celestial compass applied to autonomous outdoor robot navigation. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, (117), 40-56.
DOI: 10.1016/j.robot.2019.04.007 - Dupeyroux, J., Serres, J. R., & Viollet, S. (2019). AntBot: A six-legged walking robot able to home like desert ants in outdoor environments. Science Robotics, 4 (27), eaau0307.
DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.aau0307 - Dupeyroux, J., Viollet, S., & Serres, J. R. (2019). Polarized skylight-based heading measurements: a bio-inspired approach. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 16 (150), 20180878.
DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2018.0878
Morphological mimicry
AntBot is equipped with six legs made up of three actuators each and allowing a tripod locomotion similar to that observed in ants. The robot can walk with a maximum speed of 90 cm/s while ensuring a good stability in roll and pitch of the robot head.

(10 Dec. 2019)
Sensory mimicry
Desert ants are sensitive to polarized light from the sky: the dorsal marginal area of their compound eye consists of ommatidia showing sensitivity to polarized radiation of UV light emanating from the sky. This sensory modality was reproduced on AntBot by means of a celestial compass comprising two pixels sensitive to UV light and surmounted by rotating linear polarizing filters. Ventral optic flow vision of insects was also reproduced on AntBot using a minimalist sensor (only 12 pixels) bio-inspired and self-adaptive to changes in brightness: the M²APix (Michaelis-Menten Auto-Adaptive Pixels) sensor.
Behavioral mimicry
In order to navigate autonomously, AntBot embeds a navigation system directly inspired by the path integrator of desert ants. This vector and relative navigation mode allows the insect to merge heading information (vision of the polarized light of the sky) and distance information (combination of the ventral optical flow and step counting) to estimate at each moment its homing vector, thus giving the direction, the sense and the distance to be covered to find the nest. This system allowed AntBot to find its way back to the nest with a positioning error of about 5 cm after nearly 14 meters of travel.
Popularization of science
- Interview with Enki Bilal. Intervention by Julien Serres at the festival “Oh les beaux jours!” (2019, June).
- This little robot that navigates without GPS like an ant . Dupeyroux J., in The Conversation (2019, May).
- AntBot: an autonomous ant robot that navigates without GPS. Dupeyroux J., Serres J., & Viollet S., in La Lettre de Grand Luminy Technopôle, no. 100 (2019, May).
- A legged robot without GPS. Podcast directed by Barbara Vignaux, Universcience – Palais des Découvertes, City of Science and Industry (2019).
- AntBot, le robot fourmi. Report directed by Nicolas Baker – CNRS, February 13, 2019.
- When artificial intelligence is inspired by the living. Conference given Opera Mundi by Julien Dupeyroux (Chateauneuf-le-Rouge, November 2018).
- L’envolée scientifique. Documentary directed by Kenza Chattar of the SATIS Department (Sciences Arts and Techniques of Image and Sound) of the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Aix-Marseille (2017).


International media coverage
- This ant-inspired robot can navigate better than civilian GPS. Science
- AntBot makes its own way home. Nature Electronics
- A 6-legged robot stares at the sky to navigate like a desert ant. Wired
- Ant-inspired walking robot navigates without GPS by using polarized light. Digital Trends
- Robot mimics desert ants to find its way home without GPS. New Scientist
- Robot weet de weg zonder gps dankzij woestijnmier. de Volkskrant
- AntBot, an autonomous robot inspired by desert ants. Le Monde
- A legged robot with a sense of direction. Challenges
- An inexpensive sensor to navigate without GPS. Les Echos
- It is a remarkable innovation: this robot ant is oriented without GPS. France Inter
- The first legged robot that moves without GPS. CNRS (press release)
- Marseille: the robot inspired by the desert ant. La Provence
- A robot that moves without GPS designed in Marseille. La Marseillaise
- Here is Antbot, a robot inspired by ants and which moves without GPS. Futura Sciences
- This robot manages to orient itself thanks to the sunlight. Science et Vie
- AntBot: the very first robot to evolve without GPS to locate itself. Trust My Science
- France24 – February 22, 2019 Tech 24 Show.
- M6 – News 12.45 of February 19, 2019.
- France2 – Télématin broadcast of April 30, 2019.

